طراحی و تبیین مؤلفههای مدل فناوری بلاکچین در زنجیره تأمین پایدار مالی صنعت تولید قطعات خودرو
کلمات کلیدی:
پایداری زنجیره تامین, فناوری بلاکچین, مدلسازی ساختاری تفسیری, تامین مالیچکیده
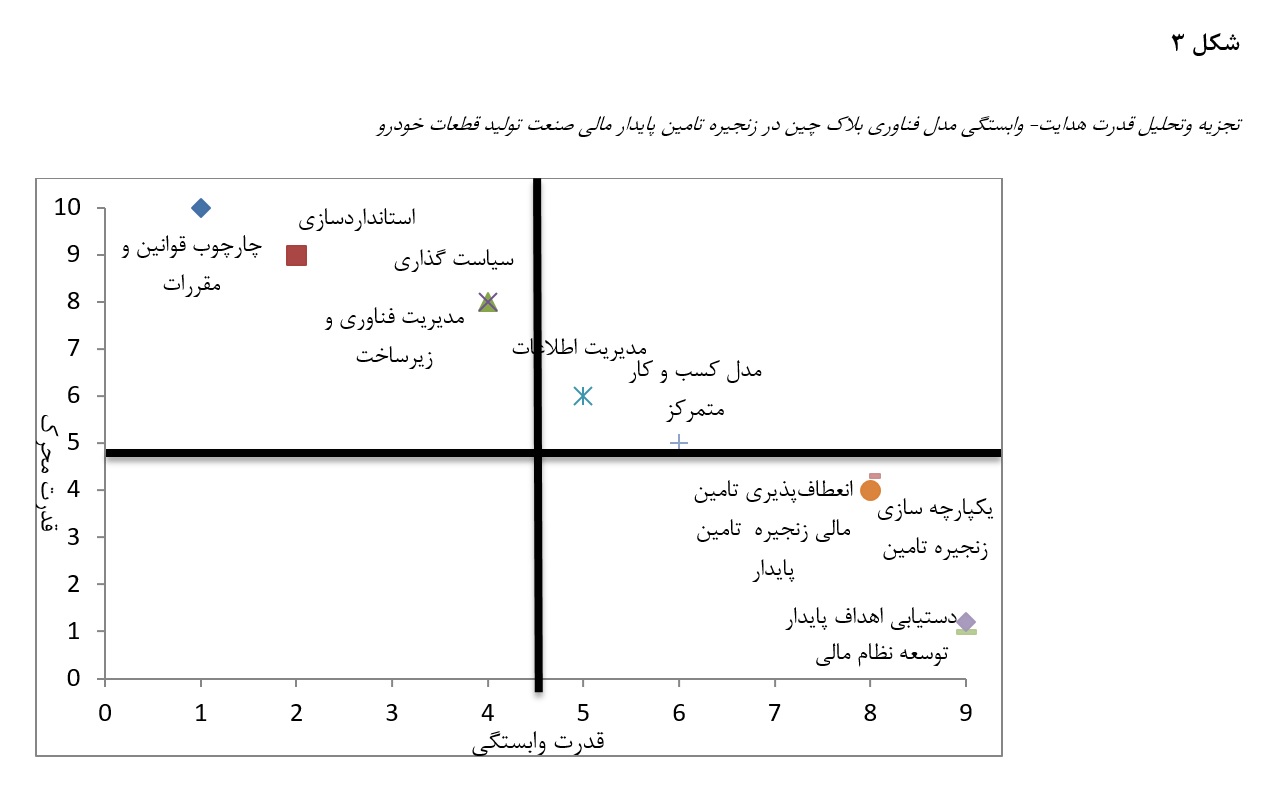
هدف این پژوهش طراحی و ارائه مدلی جامع برای بهکارگیری فناوری بلاکچین بهمنظور ارتقای پایداری مالی زنجیره تأمین در صنعت تولید قطعات خودرو است. این تحقیق از نوع آمیخته (کیفی–کمی) و از نظر هدف، کاربردی–توسعهای است. در بخش کیفی، دادهها از طریق مصاحبه نیمهساختاریافته با ۱۰ نفر از خبرگان و مدیران ارشد ۱۰ شرکت بزرگ تولیدکننده قطعات خودرو جمعآوری و با روش دادهبنیاد کدگذاری شد. سپس در بخش کمی، یافتههای کیفی با استفاده از تکنیک دلفی فازی غربالگری و تأیید گردید و پرسشنامه مقایسههای زوجی بین ۲۱۴ نفر از مدیران ارشد، مالی، فناوری و زنجیره تأمین در ۱۵۰ شرکت توزیع شد. تحلیل روابط و سطحبندی متغیرها از طریق مدلسازی تفسیری–ساختاری (ISM) و تحلیل MICMAC انجام شد. نتایج دلفی فازی منجر به شناسایی ۱۰ مؤلفه کلیدی برای بهکارگیری بلاکچین در زنجیره تأمین پایدار مالی شد، از جمله «چارچوب قوانین و مقررات»، «استانداردسازی»، «مدیریت فناوری و زیرساخت»، «سیاستگذاری»، «مدیریت اطلاعات بلاکچین»، «مدل کسبوکار متمرکز»، «یکپارچهسازی زنجیره تأمین»، «انعطافپذیری تأمین مالی»، «توسعه نظام مالی» و «دستیابی به اهداف پایدار». مدل ISM این مؤلفهها را در هفت سطح سلسلهمراتبی نشان داد؛ متغیرهای «چارچوب قوانین و مقررات» و «استانداردسازی» در سطوح پایهای و مستقل قرار گرفتند و «توسعه نظام مالی» و «دستیابی به اهداف پایدار» بهعنوان نتایج نهایی مدل شناسایی شدند. یافتهها بیانگر آن است که برای موفقیت در پیادهسازی بلاکچین در زنجیره تأمین پایدار مالی، ابتدا باید زیرساخت قانونی و استانداردها تقویت شود و سپس سیاستگذاری سازمانی و مدیریت فناوری اطلاعات توسعه یابد. این مدل میتواند راهنمایی عملی برای ارتقای شفافیت مالی، اعتماد، کاهش ریسک و دستیابی به اهداف توسعه پایدار در صنعت قطعات خودرو ارائه دهد.
دانلودها
مراجع
Alazab, M., Alhyari, S., Awajan, A., & Abdallah, A. B. (2021). Blockchain technology in supply chain management: an empirical study of the factors affecting user adoption/acceptance. Cluster Computing, 24(1), 83-101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-020-03200-4
Asante Boakye, E., Zhao, H., Kwame Ahia, B. N., & Adu-Damoah, M. (2025). Modeling the adoption enablers of blockchain technology-based supply chain financing: An integrative dual DOI-TOE analysis. Journal of the International Council for Small Business, 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1080/26437015.2024.2448980
Aslam, J., Saleem, A., Khan, N. T., & Kim, Y. B. (2021). Factors influencing blockchain adoption in supply chain management practices: A study based on the oil industry. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 6(2), 124-134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2021.01.002
Bal, M., & Pawlicka, K. (2021). Supply chain finance and challenges of modern supply chains. LogForum, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.17270/J.LOG.2021.525
Behnke, K., & Janssen, M. F. W. H. A. (2020). Boundary conditions for traceability in food supply chains using blockchain technology. International Journal of Information Management, 52, 101969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.05.025
Bolanos, R., Fontela, E., Nenclares, A., & Pastor, P. (2005). Using interpretive structural modelling in strategic decision-making groups. Management Decision, 43(6), 877-895. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251740510603619
Cao, S., Johnson, H., & Tulloch, A. (2023). Exploring blockchain-based Traceability for Food Supply Chain Sustainability: Towards a Better Way of Sustainability Communication with Consumers. Procedia Computer Science, 217, 1437-1445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.12.342
Chen, J., Cai, T., He, W., Chen, L., Zhao, G., Zou, W., & Guo, L. (2020). A blockchain-driven supply chain finance application for auto retail industry. Entropy, 22(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010095
Choi, T. M. (2020). Supply chain financing using blockchain: Impacts on supply chains selling fashionable products. Annals of Operations Research, 1-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03615-7
Fang, C., Ullah, N., Batumalay, M., Al-Rahmi, W. M., & Alblehai, F. (2025). Blockchain technology and its impact on sustainable supply chain management in SMEs. Peerj Computer Science, 11, e2466. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.2466
Guo, X., Xia, W., Feng, T., Tan, J., & Xian, F. (2024). Blockchain technology adoption and sustainable supply chain finance: The perspective of information processing theory. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 31(4), 3614-3632. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2759
Hasani, S. R., Jafarnejad Chaghushi, A., Safavi, H., & Mehregan, M. R. (2019). Designing a Sustainable Supply Chain Model with Emphasis on Behavioral Factors for Food Products in Kermanshah Province. Quarterly Journal of Strategic Management in Industrial Systems (formerly Industrial Management), 14(48), 61-73. https://journals.iau.ir/article_667999.html?lang=en
Hofmann, E., & Sertori, Y. (2020). Financial spillover effects in supply chains: do customers and suppliers really benefit? Logistics, 4(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics4010006
Jia, F., Zhang, T., & Chen, L. (2020). Sustainable supply chain Finance: Towards a research agenda. Journal of Cleaner Production, 243, 118680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118680
Kerr, W. R., & Nanda, R. (2015). Financing innovation. Annual Review of Financial Economics, 7, 445-462. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-financial-111914-041825
Kim, J. S., & Shin, N. (2019). The impact of blockchain technology application on supply chain partnership and performance. Sustainability, 11(21), 6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11216181
Kumar Singh, A., Prasath Kumar, V. R., Gholamreza, D., Saeed Reza, M., Patrick, M., & Farzad Pour, R. (2023). Investigating barriers to blockchain adoption in construction supply chain management: A fuzzy-based MCDM approach. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 196, 122849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122849
Modiri, M., H, K. S., & Z, H. D. (2017). Choosing medical tourism strategy based on SWOT and fuzzy multi-criteria decision making. https://ensani.ir/fa/article/535387/
Negi, S. (2024). A blockchain technology for improving financial flows in humanitarian supply chains: benefits and challenges. Journal of Humanitarian Logistics and Supply Chain Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/JHLSCM-10-2023-0099
Öztürk, C., & Yildizbaşi, A. (2020). Barriers to implementation of blockchain into supply chain management using an integrated multi-criteria decision-making method: a numerical example. Soft Computing, 24(19), 14771-14789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04831-w
Parung, J. (2019). The use of blockchain to support sustainable supply chain strategy. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering,
Pourabrahimi, A., Lotfi Bidehandeh, B., & Salimi, M. (2022). Improving Supply Chain Management Performance in the Context of Blockchain Technology. Thirteenth International Conference on Research in Management, Economics, and Development,
Safaie Ghadikalai, A. H., & Vedadi, M. (2015). Providing a Framework for Creating a Sustainable Supply Chain. First International Conference on Accounting, Management, and Innovation in Business, Soumeh Sara.
Sarkis, J., & Zhu, Q. (2018). Environmental sustainability and production: taking the road less travelled. International Journal of Production Research, 56(1-2), 743-759. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1365182
Sciarelli, M., Prisco, A., Gheith, M. H., & Muto, V. (2021). Factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in innovative Italian companies: an extended TAM approach. Journal of Strategy and Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSMA-02-2021-0054
Tawfeeq Saleh Al-Sammarraie, F., & Fathi, M. R. (2025). Evaluation of the Environmental Performance of Supply Chain in the Automotive Industry. Transactions on Data Analysis in Social Science, 7(1), 9-15. https://www.transoscience.ir/article_228268.html
Treiblmaier, H. (2019). Combining blockchain technology and the physical internet to achieve triple bottom line sustainability: a comprehensive research agenda for modern logistics and supply chain management. Logistics, 3(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics3010010
Wu, X. Y., Fan, Z. P., & Cao, B. B. (2021). An analysis of strategies for adopting blockchain technology in the fresh product supply chain. International Journal of Production Research, 61(11), 3717-3734. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2021.1894497
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 مجید زمانی خرمندیچالی (نویسنده); محمود مدیری; کیومرث فتحی هفشجانی, نوروز نوراله زاده (نویسنده)

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










