Designing and Explaining the Blockchain Technology Model for Financially Sustainable Supply Chains in the Automotive Parts Manufacturing Industry
Keywords:
Supply chain sustainability, blockchain technology, Interpretive structural modeling, financingAbstract
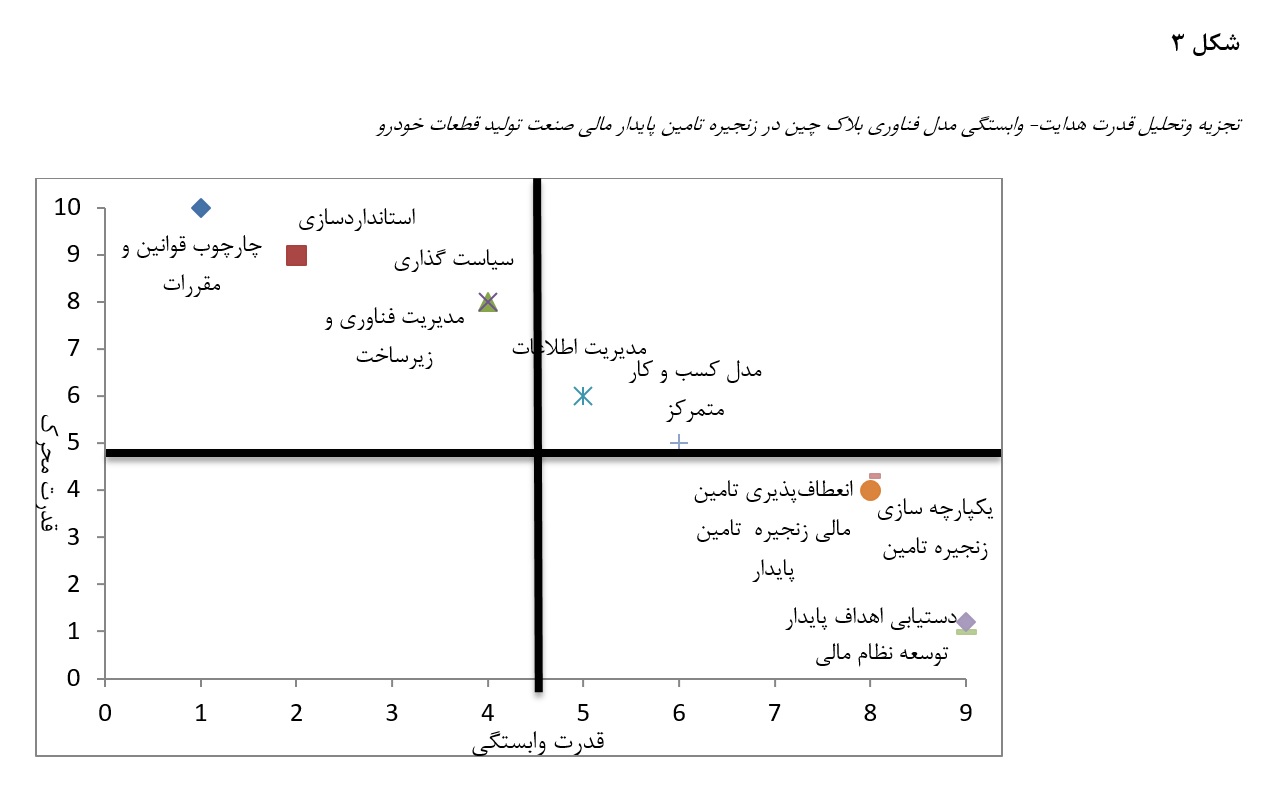
This study aimed to design and propose a comprehensive model for applying blockchain technology to enhance financial sustainability within the automotive parts manufacturing supply chain. This applied, developmental research used a mixed-methods approach. In the qualitative phase, semi-structured interviews were conducted with ten senior managers and experts from ten major automotive parts manufacturing companies, and data were analyzed using grounded theory coding. In the quantitative phase, the identified variables were validated and refined through a fuzzy Delphi technique and pairwise comparison questionnaires distributed among 214 senior, financial, IT, and supply chain managers from 150 companies. Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) and MICMAC analysis were employed to determine hierarchical relationships and driving–dependence power among components. The fuzzy Delphi analysis identified ten key components for implementing blockchain in financially sustainable supply chains, including “Legal and Regulatory Framework,” “Standardization,” “Technology and Infrastructure Management,” “Policy Making,” “Blockchain Information Management,” “Centralized Business Model,” “Supply Chain Integration,” “Financial Flexibility,” “Financial System Development,” and “Achieving Sustainable Goals.” ISM revealed a seven-level hierarchical structure, with “Legal and Regulatory Framework” and “Standardization” as foundational independent drivers, while “Financial System Development” and “Achieving Sustainable Goals” were dependent outcomes at the top. Strengthening the legal and regulatory foundation and establishing industry-wide standards are prerequisites for successful blockchain adoption in financially sustainable supply chains. Organizational policies and technology management should subsequently evolve to improve transparency, trust, and risk reduction, ultimately enabling sustainable financial systems and environmental goals in the automotive parts industry.
Downloads
References
Alazab, M., Alhyari, S., Awajan, A., & Abdallah, A. B. (2021). Blockchain technology in supply chain management: an empirical study of the factors affecting user adoption/acceptance. Cluster Computing, 24(1), 83-101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-020-03200-4
Asante Boakye, E., Zhao, H., Kwame Ahia, B. N., & Adu-Damoah, M. (2025). Modeling the adoption enablers of blockchain technology-based supply chain financing: An integrative dual DOI-TOE analysis. Journal of the International Council for Small Business, 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1080/26437015.2024.2448980
Aslam, J., Saleem, A., Khan, N. T., & Kim, Y. B. (2021). Factors influencing blockchain adoption in supply chain management practices: A study based on the oil industry. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 6(2), 124-134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2021.01.002
Bal, M., & Pawlicka, K. (2021). Supply chain finance and challenges of modern supply chains. LogForum, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.17270/J.LOG.2021.525
Behnke, K., & Janssen, M. F. W. H. A. (2020). Boundary conditions for traceability in food supply chains using blockchain technology. International Journal of Information Management, 52, 101969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.05.025
Bolanos, R., Fontela, E., Nenclares, A., & Pastor, P. (2005). Using interpretive structural modelling in strategic decision-making groups. Management Decision, 43(6), 877-895. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251740510603619
Cao, S., Johnson, H., & Tulloch, A. (2023). Exploring blockchain-based Traceability for Food Supply Chain Sustainability: Towards a Better Way of Sustainability Communication with Consumers. Procedia Computer Science, 217, 1437-1445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.12.342
Chen, J., Cai, T., He, W., Chen, L., Zhao, G., Zou, W., & Guo, L. (2020). A blockchain-driven supply chain finance application for auto retail industry. Entropy, 22(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010095
Choi, T. M. (2020). Supply chain financing using blockchain: Impacts on supply chains selling fashionable products. Annals of Operations Research, 1-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03615-7
Fang, C., Ullah, N., Batumalay, M., Al-Rahmi, W. M., & Alblehai, F. (2025). Blockchain technology and its impact on sustainable supply chain management in SMEs. Peerj Computer Science, 11, e2466. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.2466
Guo, X., Xia, W., Feng, T., Tan, J., & Xian, F. (2024). Blockchain technology adoption and sustainable supply chain finance: The perspective of information processing theory. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 31(4), 3614-3632. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2759
Hasani, S. R., Jafarnejad Chaghushi, A., Safavi, H., & Mehregan, M. R. (2019). Designing a Sustainable Supply Chain Model with Emphasis on Behavioral Factors for Food Products in Kermanshah Province. Quarterly Journal of Strategic Management in Industrial Systems (formerly Industrial Management), 14(48), 61-73. https://journals.iau.ir/article_667999.html?lang=en
Hofmann, E., & Sertori, Y. (2020). Financial spillover effects in supply chains: do customers and suppliers really benefit? Logistics, 4(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics4010006
Jia, F., Zhang, T., & Chen, L. (2020). Sustainable supply chain Finance: Towards a research agenda. Journal of Cleaner Production, 243, 118680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118680
Kerr, W. R., & Nanda, R. (2015). Financing innovation. Annual Review of Financial Economics, 7, 445-462. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-financial-111914-041825
Kim, J. S., & Shin, N. (2019). The impact of blockchain technology application on supply chain partnership and performance. Sustainability, 11(21), 6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11216181
Kumar Singh, A., Prasath Kumar, V. R., Gholamreza, D., Saeed Reza, M., Patrick, M., & Farzad Pour, R. (2023). Investigating barriers to blockchain adoption in construction supply chain management: A fuzzy-based MCDM approach. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 196, 122849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122849
Modiri, M., H, K. S., & Z, H. D. (2017). Choosing medical tourism strategy based on SWOT and fuzzy multi-criteria decision making. https://ensani.ir/fa/article/535387/
Negi, S. (2024). A blockchain technology for improving financial flows in humanitarian supply chains: benefits and challenges. Journal of Humanitarian Logistics and Supply Chain Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/JHLSCM-10-2023-0099
Öztürk, C., & Yildizbaşi, A. (2020). Barriers to implementation of blockchain into supply chain management using an integrated multi-criteria decision-making method: a numerical example. Soft Computing, 24(19), 14771-14789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04831-w
Parung, J. (2019). The use of blockchain to support sustainable supply chain strategy. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering,
Pourabrahimi, A., Lotfi Bidehandeh, B., & Salimi, M. (2022). Improving Supply Chain Management Performance in the Context of Blockchain Technology. Thirteenth International Conference on Research in Management, Economics, and Development,
Safaie Ghadikalai, A. H., & Vedadi, M. (2015). Providing a Framework for Creating a Sustainable Supply Chain. First International Conference on Accounting, Management, and Innovation in Business, Soumeh Sara.
Sarkis, J., & Zhu, Q. (2018). Environmental sustainability and production: taking the road less travelled. International Journal of Production Research, 56(1-2), 743-759. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1365182
Sciarelli, M., Prisco, A., Gheith, M. H., & Muto, V. (2021). Factors affecting the adoption of blockchain technology in innovative Italian companies: an extended TAM approach. Journal of Strategy and Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSMA-02-2021-0054
Tawfeeq Saleh Al-Sammarraie, F., & Fathi, M. R. (2025). Evaluation of the Environmental Performance of Supply Chain in the Automotive Industry. Transactions on Data Analysis in Social Science, 7(1), 9-15. https://www.transoscience.ir/article_228268.html
Treiblmaier, H. (2019). Combining blockchain technology and the physical internet to achieve triple bottom line sustainability: a comprehensive research agenda for modern logistics and supply chain management. Logistics, 3(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics3010010
Wu, X. Y., Fan, Z. P., & Cao, B. B. (2021). An analysis of strategies for adopting blockchain technology in the fresh product supply chain. International Journal of Production Research, 61(11), 3717-3734. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2021.1894497
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 مجید زمانی خرمندیچالی (نویسنده); محمود مدیری; کیومرث فتحی هفشجانی, نوروز نوراله زاده (نویسنده)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










