Designing a Structural-Interpretive Model (ISM) of The Digital Transformation Culture Barriers With a Contextual Approach In Tehran Province Water And Wastewater Company
Keywords:
Digital transformation culture, drivers, interpretive structural modeling, water and wastewater of Tehran provinceAbstract
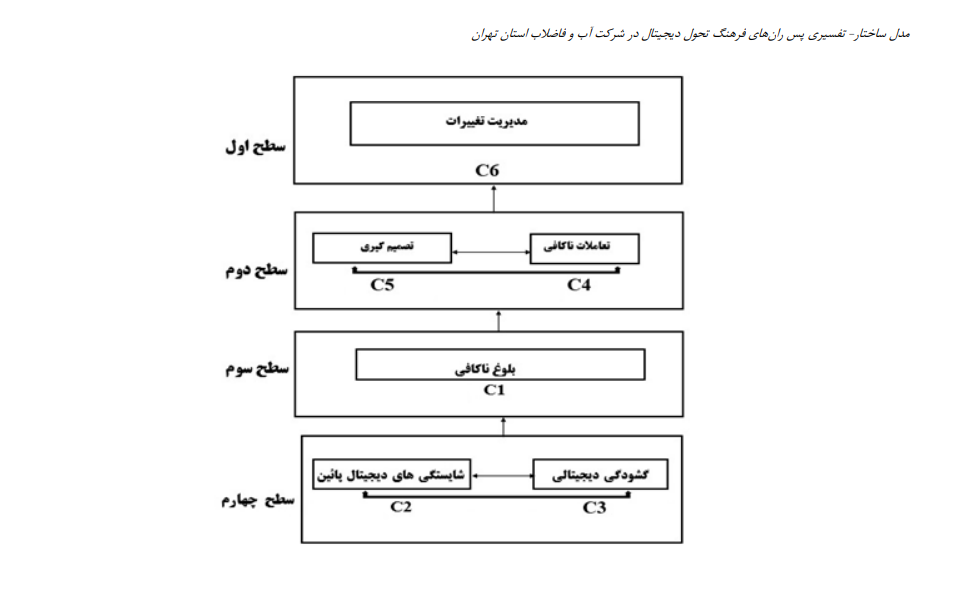
Today, digital transformation is described as a modern struggle for survival against the threat of digital disruption. Digital transformation is a process through which an organization evolves by experimenting with new technologies, revising its current approaches to problem-solving, and modifying its operational routines. To realize a digital transformation culture, it is essential to thoroughly examine and address the barriers, challenges, and barriers associated with digital disruption, the integration of emerging technologies, and the transformation of traditional work environments, as overcoming these obstacles is necessary for a successful digital transformation. The objective of this study is to design an interpretive structural model (ISM) of digital transformation culture barriers with a contextual approach in the Water and Wastewater Company of Tehran Province. This research is applied in terms of its objective and employs an exploratory mixed-method approach. In the qualitative phase, thematic analysis was utilized, while the quantitative phase employed interpretive structural modeling (ISM). The qualitative research population consisted of 14 experts, who were purposefully selected until data saturation was achieved. In the quantitative phase, a sample of 234 managers was randomly selected. Data collection in the qualitative phase was conducted through semi-structured in-depth interviews, while in the quantitative phase, a researcher-developed questionnaire was used. In the quantitative stage, data analysis was performed using descriptive statistics, confirmatory factor analysis, and interpretive structural modeling (ISM) based on the opinions of 12 experts. After identifying the themes, the model of digital transformation culture barriers was developed, and the relationships between factors were determined using interpretive structural modeling (ISM). Additionally, the factors were analyzed based on their impact and dependency using the MICMAC (Matrice d'Impacts Croisés Multiplication Appliquée à un Classement) diagram. The results indicate that digital competency and digital openness, with the highest influence power, serve as the primary barriers and key barriers to the formation of a digital transformation culture. The linking factors, including inadequate interactions and decision-making, act as inhibiting elements in the system due to their prevalence. The factor of insufficient maturity is located in the autonomous quadrant, while change management is influenced by other factors within the system. Consequently, to establish and enhance a digital transformation culture, it is necessary to review, modify, or eliminate these major barriers, as overcoming them is crucial for successful digital transformation.
Downloads
References
Babin, R., & Grant, K. A. (2019). How Do CIOs Become CEOs. Journal of Global Information Management, 27(4), 1-15. https://doi.org/10.4018/JGIM.2019100101
Ben-Zvi, T., & Luftman, J. (2022). Post-Pandemic IT: Digital Transformation and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142215275
Bendak, S., & Shikhli, A. M. (2020). How changing organizational culture can enhance innovation: Development of the innovative culture enhancement framework. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2020.1712125
Blanco, J. L., Mullin, A., Pandya, K., & Sridhar, M. (2017). The new age of engineering and construction technology. The-new-age-of-engineering-and-construction-technology.pdf
Block, C. (2022). 12 Reasons Your Digital Transformation Will Fail. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbeshumanresourcescouncil/2022/03/17/12-reasons-your-digital-transformation-will-fail
Bozkus, K. (2023). Organizational Culture Change and Technology: Navigating the Digital Transformation. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.112903
Bughin, J., Hazan, E., Ramaswamy, S., Allas, T., Dahlstrom, P., Henke, N., & Trench, M. (2017). Impact of Advancement of Technology, Competitive Pressure, User Expectation on Continuous Digital Disruption: Mediating Role of Perceive Ease of Use. https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=3043572
Buzinkay, M. (2023). 11 Digital Transformation Challenges and How to Overcome Them. https://www.identecsolutions.com/news/11-digital-transformation-challenges-and-how-to-overcome-them
Byrne, P. (2022). Digital transformation and modernization.
Cantemir, M., Pitic, A., & Bayraktar, D. (2024). Drivers of Digital Transformation and their Impact on Organizational Management. https://doi.org/10.2478/sbe-2023-0009
Chambers, J. (2019). 40% of Companies Will Be Dead in Ten Years - The Impact of Digital Transformation. https://www.hec.edu/en/executive-education/news/40-companies-will-be-dead-ten-years
Elham, A. A., Mohammadian, A., Ghateri, A. R., & Shoar, M. (2019). Presenting a Digital Transformation Capability Maturity Model Using the Meta-Synthesis Method: A Case Study of Pharmaceutical Companies. Quarterly Journal of Information Management. https://www.sid.ir/paper/381130/fa
Gao, J. (2024). Digital Transformation Path Design Research of Energy Enterprise Based on SPACE Analysis. https://doi.org/10.4108/eai.17-11-2023.2342725
Ghadousi, P. (2022). Organizational Change Management During Digital Transformation in the Construction Industry for Sustainable Urban Development. Scientific-Research Quarterly Journal of Geography and Regional Planning. https://www.jgeoqeshm.ir/article_164440.html
Hajieh, R. F., Davoud, S., & Mehri, K. (2022). Identifying and Ranking the Factors Affecting the Implementation of Digital Transformation in Technology-Oriented Organizations. Scientific Journal of "Technology, Studies, and Law Enforcement Communications". https://civilica.com/doc/1709220
Hao, J., Ren, X., Bi, H., & Wu, J. G. (2025). How does digital transformation predict the investment cycle in family enterprises? Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 210, 123895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2024.123895
Kankanam Gamage, A. N. K. (2021). Study of Challenges in Implementing Digital Transformation in Construction Projects. https://ijpsat.org/index.php/ijpsat/article/view/3912
Kaplan, A., & Haenlein, M. (2019). Digital transformation and disruption: On big data, blockchain, artificial intelligence, and other things. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2019.07.001
Koeleman, J., Ribeirinho, M. J., Rockhill, D., Sjödin, E., & Strube, G. (2019). Decoding digital transformation in construction. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/operations/our-insights/decoding-digital-transformation-in-construction
Koscheyev, V., Rapgof, V., & Vinogradova, V. (2019). Digital transformation of construction organizations. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/497/1/012010
Koseoglu, O., Keskin, B., & Ozorhon, B. (2019). Challenges and enablers in BIM-enabled digital transformation in mega projects: The Istanbul new airport project case study. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9050115
Krimpizi, T. G., Peristeras, V., & Magnisalis, I. (2023). Classification of Barriers to Digital Transformation in Higher Education Institutions: Systematic Literature Review. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13070746
Lee, H., & Lee, S. (2020). Creative industry digital transformation case study, market reorganization strategy and platform. https://doi.org/10.14400/JDC.2020.18.7.177
Lee, S., & Lee, D. (2021). Opportunities and challenges for contactless healthcare services in the post-COVID-19 Era. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120712
Malik, M. (2024). Digital Leadership, Business Model Innovation and Organizational Change: Role of Leader in Steering Digital Transformation. Benchmarking an International Journal. https://doi.org/10.1108/bij-04-2023-0283
Müller, S. D., Obwegeser, N., Glud, J. V., & Johildarson, G. (2019). Digital Innovation and Organizational Culture: The Case of a Danish Media Company. https://aisel.aisnet.org/sjis/vol31/iss2/1
Nasih, M. Z. (2024). Digital Transformation: The Effect of Learning Management Systems in Developing Employee Digital Competence. Jurnal Ekonomi Bisnis & Entrepreneurship, 18(2), 604-613. https://doi.org/10.55208/z4bv1w35
Noori, M., Shah Hosseini, M. A., Zanjani, M. S., & Abedin, B. (2019). Designing a Conceptual Framework for Digital Transformation Leadership in Iranian Organizations. Management and Planning in Educational Systems. https://mpes.sbu.ac.ir/article_98486_3249bcfce893a7e39b6eee2f0d9d9105.pdf
Parusheva, S. (2019). Digitalization and Digital Transformation in Construction-Benefits and Challenges. In. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336699474_Digitalization_and_Digital_Transformation_in_Construction_-_Benefits_and_Challenges
Pradana, M., Silvianita, A., Syarifuddin, S., & Renaldi, R. (2022). The Implication of Digital Organisational Culture on Firm Performance. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.840699
Raj, A., Dwivedi, G., Sharma, A., Jabbour, A. B. L. d. S., & Rajak, S. (2020). Barriers to the adoption of industry 4.0 technologies in the manufacturing sector: An inter-country comparative perspective. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.107546
Saatcioglu, O. (2019). Scrutinizing the Barriers That Impede Industry 4.0 Projects: A Country-Wide Analysis for Turkey. In. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-7865-9.ch016
Serpa, S., Sá, M. J., & Ferreira, C. M. (2022). Digital Organizational Culture: Contributions to a Definition and Future Challenges. https://doi.org/10.36941/ajis-2022-0095
Shahi, C., & Sinha, M. (2020). Digital transformation: challenges faced by organizations and their potential solutions. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJIS-09-2020-0157
Shirazi, M., Yazdani, H., & Matin, H. Z. (2021). Providing a Roadmap for Implementing the Required Organizational Culture for Digital Transformation Using a Meta-Synthesis Approach.
Soleimani, Z. (2021). Examining Culture Development as the Main Challenge of Digital Transformation.
Trushkina, N., Abazov, R., & Rynkevych, N. (2020). Digital Transformation of Organizational Culture under Conditions of the Information Economy. https://doi.org/10.34021/ve.2020.03.01(1)
Verlinden, N. (2023). HR Digital Transformation: An HR Leader's Guide. https://www.aihr.com/blog/hr-digital-transformation/
Wolf, M., Semm, A., & Erfurth, C. (2018). Digital transformation in companies - challenges and success factors. In. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93408-2_13
Zanjani, M. S. (2021). Digital Transformation in the Insurance Industry: What and Why. Digitigi Publishing Center, Tehran, Iran. Digital Transformation in the Insurance Industry - Dr. Mehdi Shami Zanjani's Website
Zanjani, M. S., Nabooti, A., Nasab, H. S. M., & Doost, I. S. (2020). Examining the Status of Digital Culture in the Banking Industry. Report - Examining the Status of Digital Culture in the Banking Industry.pdf
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Technology in Entrepreneurship and Strategic Management (JTESM)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










