Optimizing Bank Profitability Model Considering the Role of Modern Banking Technologies
Keywords:
Bank Optimization, Bank Profitability, Modern Banking Technologies, FintechAbstract
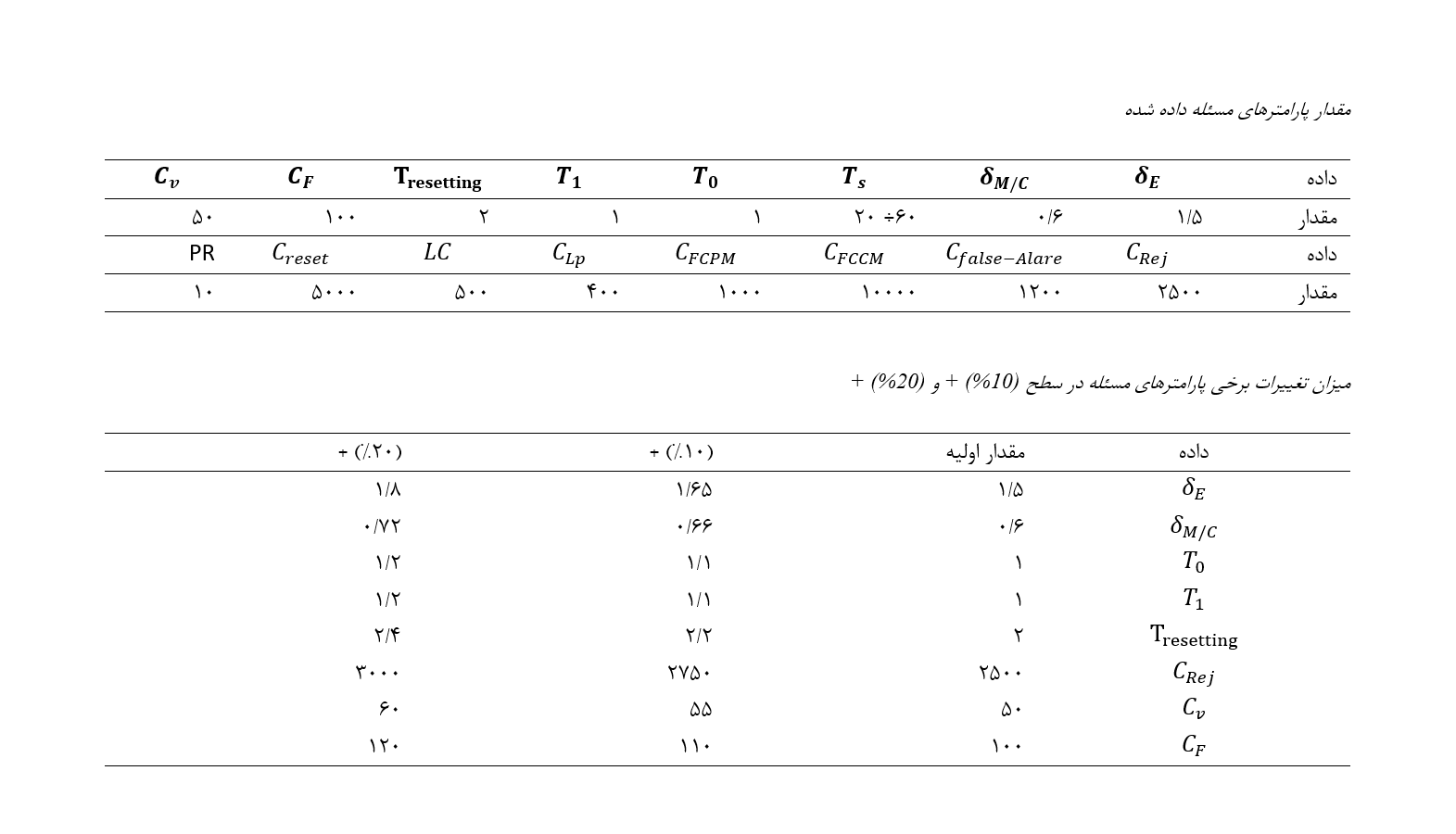
The aim of this study is to present an optimized model for bank profitability by considering the role of modern banking technologies. This research, being exploratory in nature due to its model development, is also considered applied because its results are utilized by beneficiaries. A quantitative method is used in this study to optimize bank profitability while considering the role of modern banking technologies. In the first step, influential components are identified through library techniques and document review, followed by mathematical programming for modeling. The proposed model is optimized using the epsilon-constraint algorithm in the MAPLE software and further optimized using MATLAB software. The research population, as a case study, includes documents and articles related to the banking industry. Initially, a single-component bank, considered as part of the system, was examined. Assume the bank operates in a seven-hour shift, six days a week. The maintenance activity time and fintech interventions were set to 7 time units, and the service delivery and corrective actions were set to 12 time units. With a 10% and 20% increase in the δ_E and δ_(M/C) data, significant changes in the objective function and decision variables were observed. However, changes in other data did not result in noticeable alterations in the model, indicating the importance of preventing the process from shifting to an out-of-control state and the significance of changes in the mean and standard deviation of the targeted quality characteristic. The proposed model determines the optimal value of each of the four decision variables: sample size (n), sampling interval (h), control limit coefficient (k), and intervals for preventive fintech actions (t_PM), which minimizes the total expected cost from integration per time unit. A numerical example demonstrated the economic impact of cost parameters on the integrated policy of profit control and preventive fintech actions. Additionally, in this study, the integrated model was compared with the independent model through a numerical example, and the significant difference in total cost highlighted the superiority of the integrated model over the independent model.
Downloads