Identifying the Driving Forces Affecting the Development of the Government's Revenue Portfolio
Keywords:
government revenue portfolio, futures studies, development, policymakingAbstract
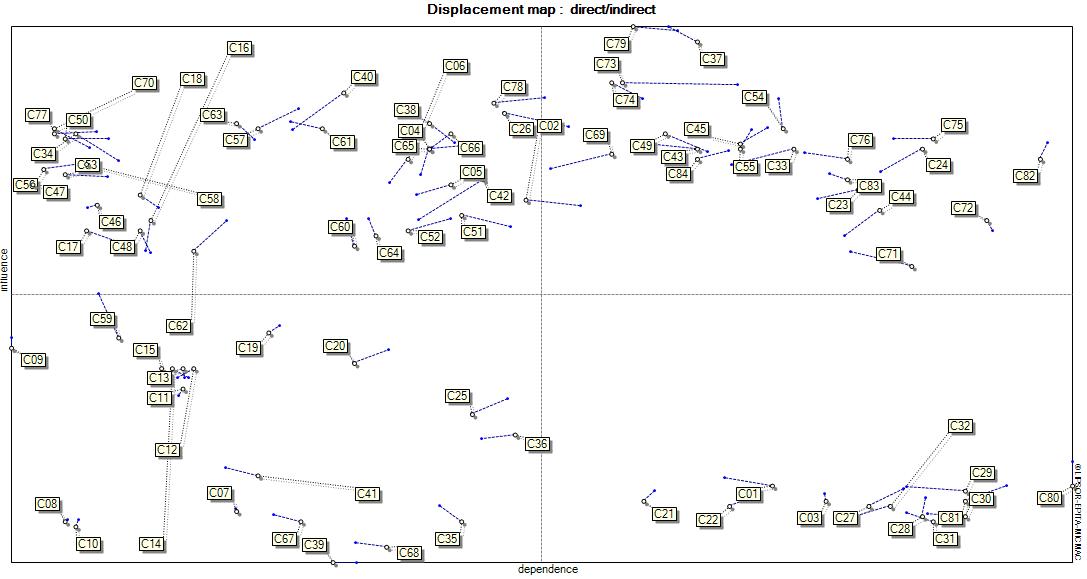
The present study aims to formulate policies for developing the government's revenue portfolio using a futures research approach. This research seeks to identify and explore possible futures and scenarios for the development of the government's revenue portfolio and strives to formulate strategies based on the most desirable scenarios. The study falls within the domain of futures research and is classified as qualitative research, utilizing the scenario-writing method. The statistical population of this study includes "experts in the fields of economics and policymaking" categorized into three groups: (a) academic elites, (b) economic managers and decision-makers, and (c) economic decision-makers in parliament. After selecting the experts, a structured inquiry process was conducted to collect their views regarding the government's revenue portfolio. Ultimately, after screening the variables, 84 variables were identified within eight dimensions as the primary macro variables affecting the government's revenue portfolio: legal factors, cultural and social factors, economic factors and sub-sectors, global and international factors, structural factors, banking and financial factors, science and knowledge-related factors, and political factors. Subsequently, using the cross-impact analysis (structural analysis) method through MICMAC software, the key influencing factors shaping the future state of the studied environment were analyzed. Based on this analysis, the key influencing variables affecting the development of the government's revenue portfolio include natural gas and petrochemical industries, agricultural economy, inflation rate, labor market conditions and employment levels, stock prices and stock exchange performance, free trade zones, tax return conditions and amounts, consumption tax rates, interest rates, non-financial government revenues, locomotive industry, heavy industries (steel, electricity, and automobile manufacturing), income tax rates, tariffs and various production and employment barriers, traffic economy, foreign investment inflows, housing market conditions and prices, textile industries, construction and urban development, unemployment rate, and government revenues from natural resources.
References
A. Herati, T. Mohammadi, and A. Shahmoradi, "The role of the government income portfolio in increasing tax equity," Public Finance Journal, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 7-28, 2016.
S. L.-Y. Cheah and Y.-P. Ho, "Effective industrial policy implementation for open innovation: The role of government resources and capabilities," Technological Forecasting and Social Change, vol. 151, p. 119845, 2020/02/01/ 2020.
M. Eyshi Ravandi, M. Moeinaddin, A. Taftiyan, and M. Rostami Bashmani, "Investigating the Impact of Investor Sentiment and Liquidity on Stock Returns of the Iranian Stock Exchange," (in en), Dynamic Management and Business Analysis, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 40-52, 2024, doi: 10.22034/dmbaj.2024.2038046.1068.
A. Jafari, "Government income portfolio: Challenges and strategies," ed, 2019.
R. Vaez and M. Mohammadi, "A model for evaluating public policies in Iran (A study of the value-added tax policy)," Prospects of Public Management, vol. 29, no. 8, pp. 24-47, 2018.
A. Dehghan Herati, H. Mehrabi Basharabi, and A. Rahbar Dehghan, "Investigating the impact of fiscal and tax policies on agricultural trade in Iran," Planning and Budgeting, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 111-128, 2014.
Y. Zhang, X. Zhao, Y. Zuo, L. Ren, and L. Wang, "The development of the renewable energy power industry under feed-in tariff and renewable portfolio standard: A case study of China's photovoltaic power industry," Sustainability, vol. 9, no. 4, p. 532, 2017, doi: 10.3390/su9040532.
A. Hamidi, A. Faghihi, and K. Teimoornezhad, "Identifying and Ranking Factors Affecting Policymaking of Public Administrators' Education," Public Management Researches, vol. 16, no. 62, pp. 63-96, 2024, doi: 10.22111/jmr.2022.42740.5807.
J. Dai, Z. Ahmed, R. Alvarado, and M. Ahmad, "Assessing the nexus between human capital, green energy, and load capacity factor: policymaking for achieving sustainable development goals," Gondwana Research, vol. 129, pp. 452-464, 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2023.04.009.
H. Golabchi, M. Kiaee, and M. J. Kameli, "Designing a Superior Service Delivery Model in Education to Enhance Public Satisfaction," (in eng), Iranian Journal of Educational Sociology, Research Article vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 189-197, 2024, doi: 10.61838/kman.ijes.7.1.18.
S. H. Kazemi, E. Ahmadi, and M. Mortazavi, "Obstacles and Opportunities for Effective Implementation: A Case Study of COVID-19 Crisis Policy in Kurdistan Province," dpmk, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 528-545, 2024, doi: 10.32598/DMKP.13.4.774.1.
R. R. Bhandary and K. S. Gallagher, "What drives Pakistan's coal-fired power plant construction boom? Understanding the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor's energy portfolio," World Development Perspectives, vol. 25, p. 100396, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.wdp.2022.100396.
Z. Ying, Z. Xin-gang, J. Xue-feng, and W. Zhen, "Can the Renewable Portfolio Standards improve social welfare in China's electricity market?," Energy Policy, vol. 152, p. 112242, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112242.
K. Uno, The history of Japan's economic development: The sources of private sector dynamics and political competence, Translated by N. Pourrostami ed. Tehran: University of Tehran, University Press Institute, 2020.
A. Ali, F. A. Alsulaiman, K. Irshad, M. Shafiullah, S. A. Malik, and A. H. Memon, "Renewable Portfolio Standard from the Perspective of Policy Network Theory for Saudi Arabia Vision 2030 Targets," in 2021 4th International Conference on Energy Conservation and Efficiency (ICECE), 2021: IEEE, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/ICECE51984.2021.9406286.
S. M. Al-Kahtani, "Environmental Responsibility, Strategy, and Competitive Advantage: Mediating Effect of Environmental Innovation," International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 316-331, 2024, doi: 10.32479/ijeep.15482.
J. Keim, "Depolarizing innovation: Dynamic policy implications for entrepreneurial ecosystems in second-tier European regions," Junior Management Science (JUMS), vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 1211-1240, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/290633/1/1884465242.pdf.
R. K. Kumar et al., "Innovation dynamics within the entrepreneurial ecosystem: a content analysis-based literature review," Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, vol. 11, no. 1, p. 366, 2024/03/06 2024, doi: 10.1057/s41599-024-02817-9.
P. Ordóñez de Pablos, "Editorial: “Digital transformation, innovation and competitiveness: some insights from Asia”," Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 1-5, 2024, doi: 10.1108/JSTPM-01-2024-222.
E. Seifi, A. Ahmadi, and M. Moazzami, "Identifying the dimensions and components of the application of new technologies in the fourth generation university," (in en), Management and Educational Perspective, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 24-51, 2024, doi: 10.22034/jmep.2024.426783.1282.
Z. Sepidbar, Y. Mohammadzadeh, and V. Nikpey Pesyan, "Analysis of the effect of entrepreneurship index on employment in Iranian provinces: Spatial econometric approach," (in eng), The Economic Research (Sustainable Growth and Development), vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 285-311, 2024, doi: 10.22034/24.1.285.
X. H. Song et al., "Impacts of renewable portfolio standards on multi-market coupling trading of renewable energy in China: A scenario-based system dynamics model," Energy Policy, vol. 159, p. 112647, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112647.
N. P. Nguyen and E. Mogaji, "Universities' endowments in developing countries: The perspectives, stakeholders and practical implications," in Re-imagining Educational Futures in Developing Countries: Palgrave Macmillan, Cham, 2022, pp. 261-282.
A. Perdana and N. B. Mulyono, "Purchasing Strategies in the Kraljic Portfolio Matrix-a Case Study in Open Pit Coal Mining," Indonesian Mining Professionals Journal, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 45-58, 2021, doi: 10.36986/impj.v3i1.41.
A. A. Pour Ezzat, A. H. Behrouz, F. Dezhpasand, and M. Amiri, "A pathology of budgeting for research and technology in Iran using the Fuzzy-Analytic Hierarchy Process method," Innovation Management, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 85-122, 2019.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Management Strategies and Engineering Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.











