Identification of Indicators, Components, and Dimensions of the Curriculum of Successful Startups in Iran
Keywords:
Startup, Curriculum, PhenomenologyAbstract
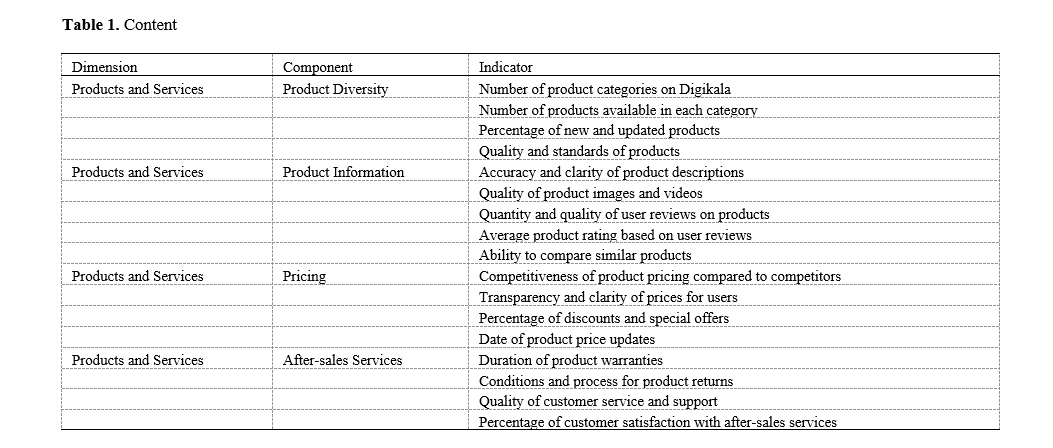
The present study aimed to identify the indicators, components, and dimensions of the curriculum of successful startups in Iran. The research method, in terms of purpose, was fundamental-applied, and in terms of data type, it was qualitative. From a paradigmatic perspective, the study falls within interpretive paradigms. The research population included scientific documents as well as academic and organizational experts. A non-random purposive sampling method was used to select interviewees based on the inclusion criteria. Data were collected through semi-structured interviews. To assess validity, four criteria—credibility, dependability, transferability, and confirmability—were employed. The reliability of the research instrument was evaluated and confirmed using the inter-coder agreement method. In this study, hermeneutic (interpretive) phenomenology, with an emphasis on Van Manen’s approach, was utilized to explore the lived experiences of startup managers and experts regarding the phenomenon of startup curriculum. The curriculum of successful startups in Iran encompasses the dimensions of innovation and creativity, business management and strategy, product development, human resource management and team building, marketing, and sales. Additionally, to improve the curriculum, several recommendations were proposed, including aspects related to innovation culture, skills training and development, long-term strategy formulation, the use of project management tools, market research, continuous testing and improvement, talent acquisition and retention, professional development training, precise budgeting, legal consulting, digital marketing utilization, and data analysis. The findings of this study can contribute to a more precise understanding of the curriculum of successful startups in Iran and, by providing a comprehensive explanation, enhance startup curricula in Iran. These outcomes are of significant importance to research beneficiaries, including managers, policymakers, and startup investors, as they can lead to optimal decision-making and the improvement of managerial and supervisory strategies.
References
M. Mohammadi and M. Khobreh, "A model for mutual decision-making between startups and venture capitalists," Industrial Management, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 359-390, 2022.
H. Aghazadeh, M. Haghighi, M. S. Torkestani, and M. S. Zarei, "Investigating the process and factors affecting brand building of startups in Iran: A multiple case study," Business Management, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 27-53, 2023.
O. S. Joel, A. T. Oyewole, O. G. Odunaiya, and O. T. Soyombo, "Navigating the digital transformation journey: Strategies for startup growth and innovation in the digital era," International Journal of Management & Entrepreneurship Research, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 697-706, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.51594/ijmer.v6i3.881.
S. Chahreh, M. A. Sarlak, and A. Rahimian, "Developing a model for improving the performance of startup accelerators," Quarterly Journal of Public Organization Management, vol. 12, no. 46, 2024.
S. Karthiga and R. Subhashni, "Cultivating entrepreneurship and startup culture: A case study of Thiagarajar College of Engineering," Journal of Engineering Education Transformations, vol. 37, no. Special Issue 2, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.16920/jeet/2024/v37is2/24075.
K. Al Omoush, C. Lassala, and S. Ribeiro-Navarrete, "The role of digital business transformation in frugal innovation and SMEs’ resilience in emerging markets," International Journal of Emerging Markets, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 366-386, 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOEM-12-2022-1937.
M. H. Moradi, M. R. Abdoli, N. Salehi, H. Valiyan, and M. Safarigrayeli, "Foresight of the driving forces of startup financing based on libertarian philosophical strategies (metaphysics) of capital market companies," Financial Research, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 758-790, 2024.
S. H. Sudaryana, B. Wirjodirdjo, and A. Windrarto, "A systematic literature review of digital startup business dynamics and policy interventions," Cogent Business & Management, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 2440636, 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2024.2440636.
D. D. Beke, A. Sólyom, and A. Juhászné Klér, "What managers can learn from knowledge-intensive technology startups: Exploring the skillset for developing adaptive organizational learning capabilities of a successful startup enterprise in management education," Society and Economy, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 68-90, 2023.
B. Jamshidi Naqani, "An empirical study of machine learning algorithms for predicting startup success," Technology Management, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 12-25, 2024.
S. Kohan Ghaziani, "Startups: Explaining entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurial intention," Management and Accounting in the Third Millennium, vol. 20, pp. 233-240, 2022.
V. Popov, "Shift in paradigm: Startup business-incubation at universities during the educational discipline inside of curriculum rather than extracurricular activities of students," Scientific Journal of Astana IT University, pp. 48-60, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.37943/WDNE3944.
Z. Queen, A. Anjani, and A. G. Prawiyog, "Designing a digital business study program using lean startup methodology," Startupreneur Business Digital (SABDA Journal), vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 1-9, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.33050/sabda.v3i1.434.
S. Taheri Zadeh and R. Shabani, "Localized curriculum: An undeniable necessity for multi-grade classrooms," Research in Curriculum Planning, vol. 63, pp. 66-77, 2019.
P. Chen, M. Clark, M. Sharma, Y. Troya, I. Cenzer, and J. Rivera, "A longitudinal workplace-based interprofessional curriculum for graduate learners in a geriatrics patient-centered medical home," Journal of Interprofessional Education & Practice, vol. 24, p. 100459, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xjep.2021.100459.
V. Tiberius and M. Weyland, "Enhancing higher entrepreneurship education: Insights from practitioners for curriculum improvement," The International Journal of Management Education, vol. 22, no. 2, p. 100981, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2024.100981.
A. Tayebi, M. Karimi Zand, and S. A. Heydari, "The impact of internal marketing on entrepreneurial orientation based on knowledge-based production and job creation in the political community of Iran (Case study: Startup businesses in Tehran)," Political Sociology of Iran, vol. 20, pp. 1613-1633, 2022.