Examining a Novel Method of Earnings Management During Inventory Investment Reduction and Its Relationship with Firm Size and Life Cycle Through the Adjustment of the Modern Capital Structure Theory in the Tehran Stock Exchange and Iran Over-the-Counter
Keywords:
Adjustment of the Modern Capital Structure Theory, Inventory Investment, Firm Size, Firm Life Cycle, Earnings Management.Abstract
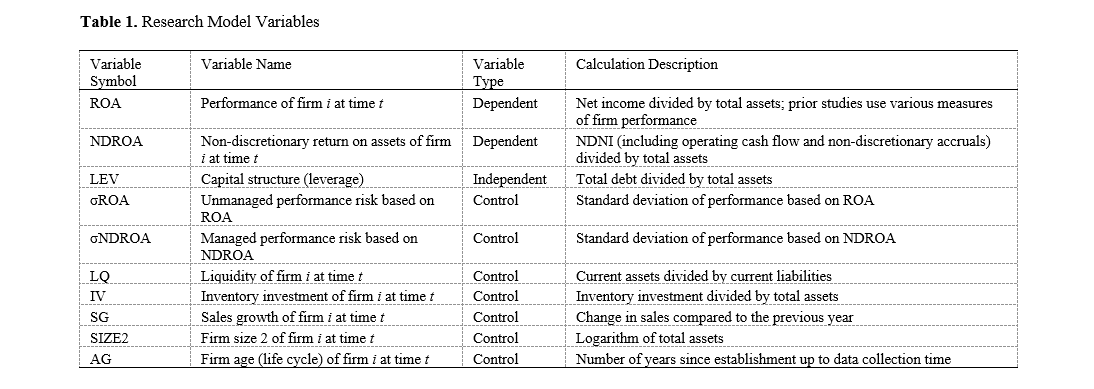
Previous research has not examined earnings management during inventory investment reduction, nor the impact of capital structure on managed and unmanaged performance. Therefore, the main objective of this study is to investigate novel methods of earnings management during reductions in inventory investment using discretionary and non-discretionary accruals, and to divide performance into two components: (1) managed performance, where the manager has the ability to employ discretionary accruals, and (2) unmanaged performance, where the manager lacks the ability to utilize discretionary accruals. Subsequently, we examined the level of insignificance, which indicates the adjustment of capital structure theories in favor of managers’ opportunistic earnings management. The statistical sample of this research includes 173 companies listed on the Tehran Stock Exchange and Iran Over-the-Counter. The research findings indicate a significant positive relationship between risk, liquidity, and firm size 2, and a negative relationship between leverage and both managed and unmanaged performance. Consequently, due to the lack of a significant relationship between inventory investment, firm size 1, and firm life cycle with managed and unmanaged performance, this indicates that an adjustment has occurred in the capital structure theory, representing opportunistic earnings management. A comparison of the managed and unmanaged performance models in this study revealed that in Iranian firms, when inventory investment decreases, managers reduce liquidity through discretionary accruals, and present firm size 1, firm life cycle, and operational history as increased, and firm size 2 as decreased, to engage in opportunistic earnings management.
References
M. Z. Frank and V. K. Goyal, "Testing the pecking order theory of capital structure," Journal of Financial Economics, vol. 67, no. 2, pp. 217-248, 2003, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-405X(02)00252-0.
M. T. Leary and M. R. Roberts, "Do firms rebalance their capital structures?," The Journal of Finance, vol. 60, no. 6, pp. 2575-2619, 2005, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.2005.00811.x.
A. N. Berger and E. B. Di Patti, "Capital structure and firm performance: A new approach to testing agency theory and an application to the banking industry," Journal of Banking & Finance, vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 1065-1102, 2006, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2005.05.015.
R. Deesomsak, K. Paudyal, and G. Pescetto, "The determinants of capital structure: Evidence from the Asia Pacific region," Journal of Multinational Financial Management, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 387-405, 2004, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mulfin.2004.03.001.
A. N. Berger and E. B. d. Patti, "Capital structure and firm performance: A new approach to testing agency theory and an application to the banking industry," 2002, doi: https://doi.org/10.17016/feds.2002.54.
I. A. Strebulaev, "Do tests of capital structure theory mean what they say?," The Journal of Finance, vol. 62, no. 4, pp. 1747-1787, 2007, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.2007.01256.x.
J. Abor, "The effect of capital structure on profitability: An empirical analysis of listed firms in Ghana," The Journal of Risk Finance, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 438-445, 2005, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/15265940510633505.
J. Abor, "Debt policy and performance of SMEs: Evidence from Ghanaian and South African firms," The Journal of Risk Finance Incorporating Balance Sheet, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 364-379, 2007, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/15265940710777315.
I. E. S. Ebaid, "The impact of capital-structure choice on firm performance: Empirical evidence from Egypt," The Journal of Risk Finance, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 477-487, 2009, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/15265940911001385.
H. Shi, H. Liu, and Y. Wu, "Are socially responsible firms responsible to accounting? A meta-analysis of the relationship between corporate social responsibility and earnings management," Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 311-332, 2024, doi: 10.1108/JFRA-06-2021-0171.
M. S. Nuhu, Z. Ahmad, and L. Y. Zhee, "Nexus Among Disclosure Quality, Discretionary Accruals and Real Earnings Management Practices: An Empirical Analysis of Malaysian Public Firms," Journal of Corporate Accounting & Finance, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 121-138, 2024, doi: 10.1002/jcaf.22720.
D. Rahman, M. Kabir, and B. Oliver, "Does exposure to product market competition influence insider trading profitability?," Journal of Corporate Finance, vol. 66, p. 101792, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2020.101792.
F. Sohailifar, M. R. Ahmadi, A. Jorjorzadeh, and S. Nasiri, "Deviation from the optimal capital structure and inefficiency of business unit investments," Accounting Knowledge, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 107-137, 2020.
L. Gan, W. Lv, and Y. Chen, "Capital structure adjustment speed over the business cycle," Finance Research Letters, vol. 39, p. 101574, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2021.101574.
B. Jonsson, "Does the size matter? The relationship between size and profitability of Icelandic firms," Bifröst Journal of Social Science, vol. 1, 2008.
K. Li, J. Niskanen, and M. Niskanen, "Capital Structure and Firm Performance in European SMEs: Does Credit Risk Make a Difference?," Managerial Finance, vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 582-601, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/MF-01-2017-0018.
A. Saeedi and I. Mahmoodi, "Capital structure and firm performance: Evidence from Iranian companies," International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, vol. 70, pp. 20-29, 2011.
A. Aflatuni, "The impact of deviation from the target capital structure on firm value," Financial Management Outlook, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 9-31, 2019.
U. M. Tanko, "Financial attributes and corporate tax planning of listed manufacturing firms in Nigeria: moderating role of real earnings management," Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JFRA-05-2022-0198.
R. Mubeen, D. Han, J. Abbas, and I. Hussain, "The effects of market competition, capital structure, and CEO duality on firm performance: A mediation analysis by incorporating the GMM model technique," Sustainability, vol. 12, no. 3840, pp. 1-18, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083480.
A. Aflatuni and M. Amin Amir Bakhtiari, "The role of disclosure quality and the quality of accruals in reducing deviations from the optimal capital structure," Asset Management and Financial Supply, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 167-180, 2017.
S. Z. Nazari Ardabili, P. Benisi, and H. Vatankhah, "Designing the Maturity Management Model of Educational Technology in Iranian Schools," Sociology of Education, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 314-326, 2024, doi: 10.22034/ijes.2024.2022649.1536.
I. L. Indomo and A. W. Lubis, "Capital structure behaviour among Indonesian property developers during different business cycles," Journal of Financial Management of Property and Construction, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 91-106, 2023.
M. Ugur, E. Solomon, and A. Zeynalov, "Leverage, competition and financial distress hazard: Implications for capital structure in the presence of agency costs," Economic Modelling, vol. 108, p. 105740, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2021.105740.
Y. Kim, S. Choi, and B.-J. Kim, "How Does a Firm’s Earnings Response Coefficient Vary with Managerial Ability? Evidence from Korea," Emerging Markets Finance and Trade, vol. 59, no. 4, pp. 1104-1114, 2023/03/16 2023, doi: 10.1080/1540496X.2022.2128750.
A. Shamsad, "The impact of financial leverage and product competition on financial distress risk: Consequences of capital structure in the presence of agency costs," Journal of Financial Studies, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 56-68, 2023.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Management Strategies and Engineering Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.











